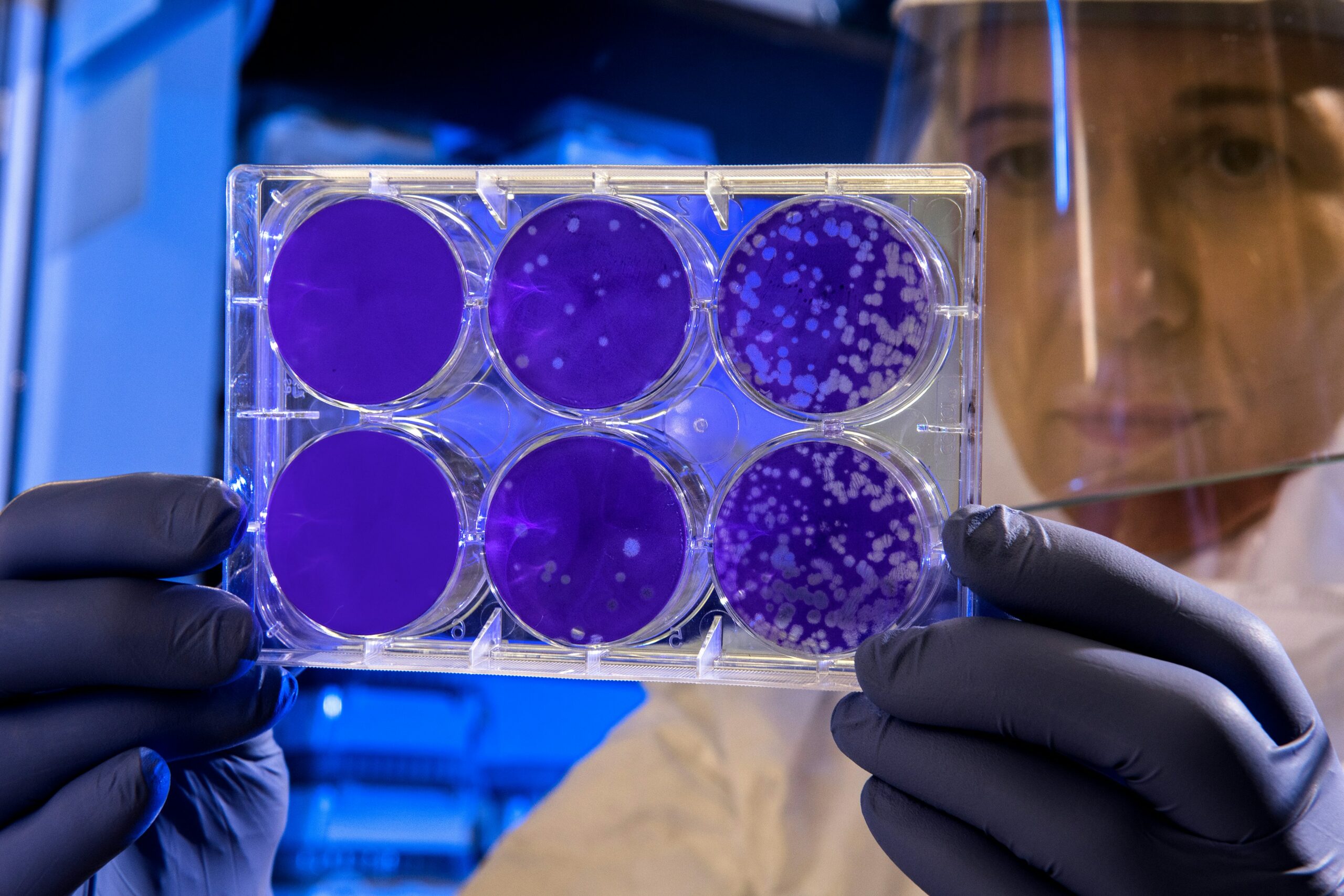
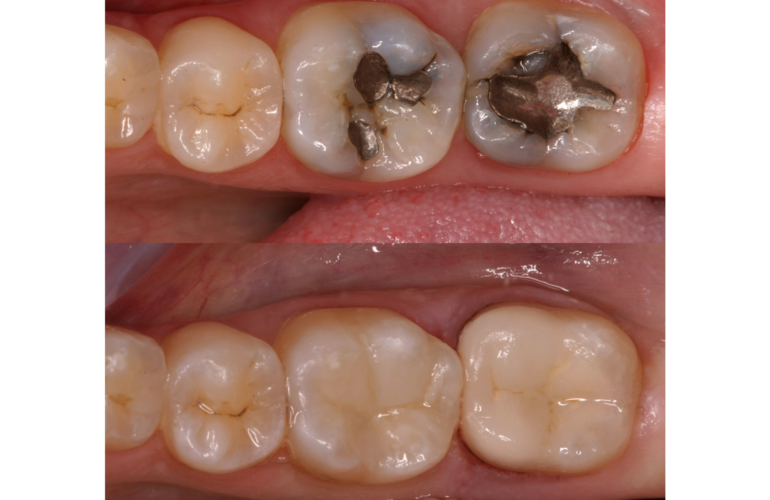
The field of regenerative medicine has made remarkable strides in recent years, with stem cell research leading the charge. In the realm of dentistry, stem cells are emerging as a groundbreaking solution for regenerating dental tissues and even entire teeth. This innovative approach promises to revolutionize dental care, offering new hope for patients with lost or damaged teeth.
What are Stem cells?
Stem cells are unique cells with the potential to develop into various types of cells and tissues.
They possess the remarkable ability to self-renew and differentiate into specialized cells, making them a valuable resource for regenerative therapies.
In dentistry, two primary types of stem cells are of particular interest: dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) and periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSCs). These cells are harvested from the dental pulp of extracted teeth or from the tissues surrounding the teeth, respectively.
How can stem cells help in Regenerating Dental Tissues?
One of the most exciting applications of stem cell research in dentistry is the regeneration of dental tissues.
Dental pulp, the soft tissue inside the tooth, is vital for maintaining tooth vitality and function. Damage or infection to the dental pulp often necessitates root canal therapy or tooth extraction. However, stem cell therapy offers a potential alternative by enabling the regeneration of healthy dental pulp tissue.
Research has demonstrated that DPSCs can differentiate into odontoblast-like cells, which are responsible for forming dentin—the hard tissue beneath the tooth enamel. By utilizing these stem cells, scientists are developing techniques to repair and regenerate damaged dental pulp, potentially restoring the natural function and health of the tooth. This advancement could significantly reduce the need for root canals and improve the overall longevity of teeth affected by trauma or decay.
What are the Advancements in Tooth Regeneration?
Beyond tissue repair, stem cells hold promise for complete tooth regeneration. Traditionally, lost teeth have been replaced with dentures, bridges, or implants. While these solutions are effective, they do not replicate the natural structure and function of a real tooth. Stem cell research aims to address this by regenerating entire teeth from the root up.
In recent studies, scientists have successfully grown tooth-like structures using stem cells. By combining DPSCs with a supportive scaffold and growth factors, researchers have been able to cultivate structures that resemble natural teeth. These tooth-like structures are not yet fully functional teeth but represent a significant step towards the development of bioengineered teeth.
What is Periodontal Regeneration?
Stem cells also offer potential in regenerating periodontal tissues, which are crucial for supporting and anchoring teeth. Periodontal disease, a common condition affecting the gum and bone tissues, can lead to tooth loss if not properly managed. Traditional treatments often involve scaling and root planting or surgical interventions to manage the disease and restore some level of tissue health.
Recent advancements in stem cell therapy are focusing on regenerating periodontal tissues, such as the periodontal ligament and alveolar bone. PDLSCs have shown the capability to regenerate these tissues, potentially reversing damage caused by periodontal disease. This regenerative approach could lead to new treatments that not only manage but also repair and restore the supporting structures of the teeth.
What do we need to look out for?
Despite the promising developments, several challenges remain in translating stem cell research into routine clinical practice. Ensuring the safety and efficacy of stem cell treatments, addressing potential ethical concerns, and managing the complexity of integrating regenerative therapies into existing dental practices are ongoing areas of research.
However, the future of stem cell therapy in dentistry looks promising. As research continues to evolve, we can expect further advancements in techniques and applications, potentially leading to innovative treatments that offer patients the opportunity to restore their dental health more effectively than ever before.
In conclusion, stem cell research represents a groundbreaking frontier in regenerative dentistry. The potential to regenerate dental tissues and entire teeth holds the promise of transforming dental care, providing solutions that not only repair but also restore natural function. As science continues to advance, stem cell therapies are poised to become a cornerstone of modern dental practice, offering hope and improved outcomes for patients worldwide.